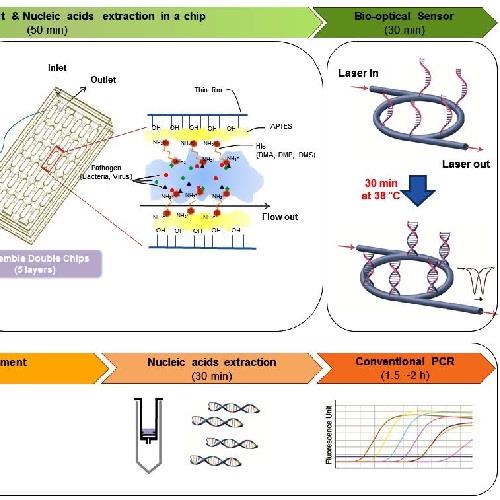
An isothermal based recombinase polymerase amplification assay for rapid, sensitive and robust indexing of citrus yellow mosaic virus.
The results from the present study indicated that RPA assay can be used easily in routine indexing of citrus planting material. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first report on development of a rapid and simplified isothermal detection assay for CYMV and can be utilized as an effective technique in quarantine and budwood certification process.