Rapid and sensitive detection of canine distemper virus by real-time reverse transcription recombinase polymerase amplification
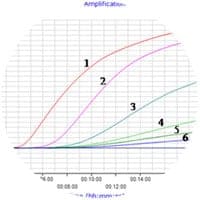
The RT-RPA assay was performed successfully at 40 °C, and the results were obtained within 3 min–12 min. The assay could detect CDV, but did not show cross-detection of canine parvovirus-2 (CPV-2), canine coronavirus (CCoV), canine parainfluenza virus (CPIV), pseudorabies virus (PRV) or Newcastle disease virus (NDV), demonstrating high specificity.