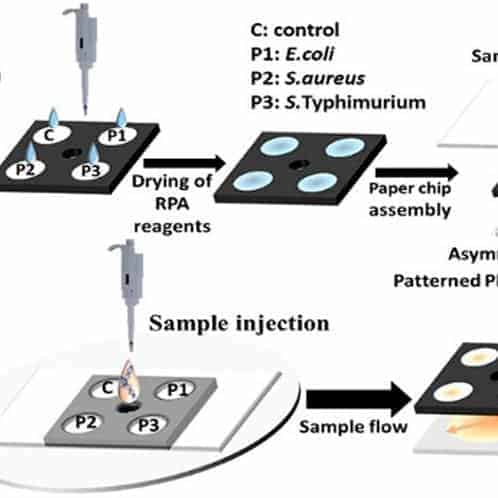
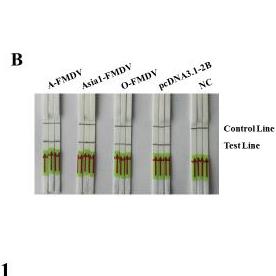
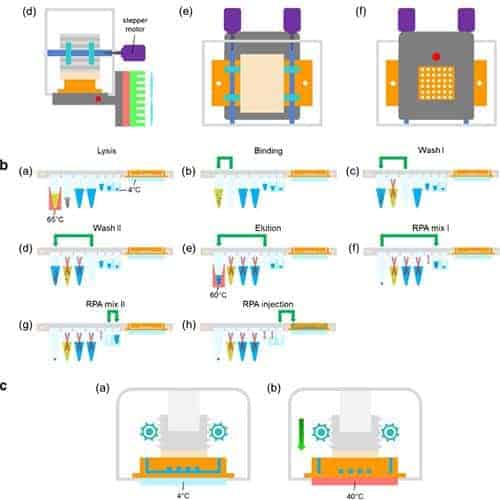
Rapid detection of avian influenza A virus (H7N9) by lateral flow dipstick-recombinase polymerase amplification.
In this study, a lateral flow dipstick recombinase polymerase amplification (LFD-RPA) assay for rapid detection of both hemagglutinin and neuraminidase gene of H7N9 was developed and evaluated. The H7-LFD-RPA and N9-LFD-RPA assay were able to detect 32 fg H7N9 nucleic acid which is more convenient and rapid than previous methods.