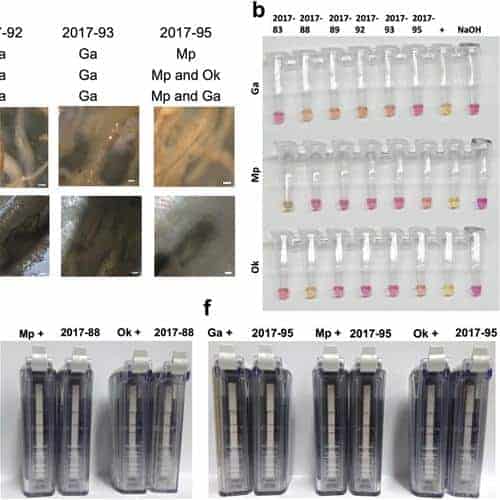
Detection of root-infecting fungi on cool-season turfgrasses using loop-mediated isothermal amplification and recombinase polymerase amplification.
Take-all patch, necrotic ring spot, and summer patch are destructive diseases of amenity turfgrasses in temperate climates. LAMP and RPA assays were created for each of the causal agents of the above diseases. Both assays were highly specific to each pathogen and consistently amplified the target organism. RPA assays in general demonstrated a lower tendency for false positive results in […]